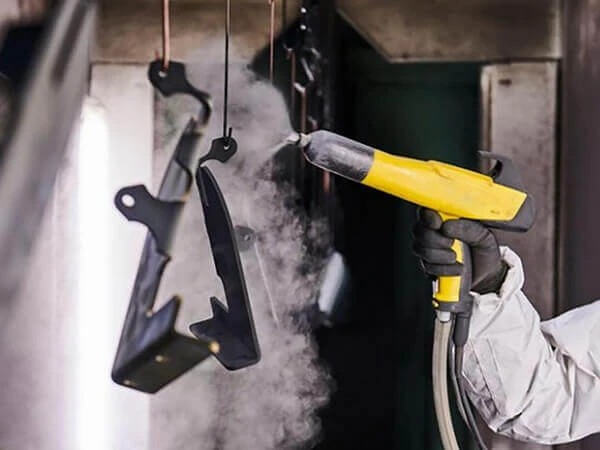
How to cut sheet metal?
One of the four methods of fabricating sheet metal is cutting. The most common sheet metal techniques are laser and water jet cutting.
What is laser cutting?
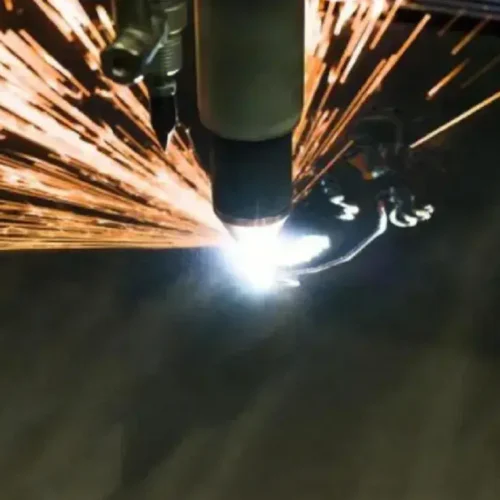
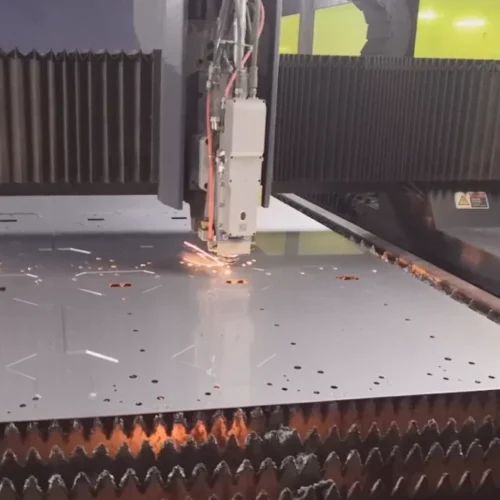
Laser cutting is a thermal process that utilizes a high-power light beam(i.e., a laser cutter), which melts the materials apart. Laser cutting is efficient in manufacturing precise industrial sheet metal, and it has low energy consumption though it may struggle to penetrate thicker or small gauges of sheet metal.
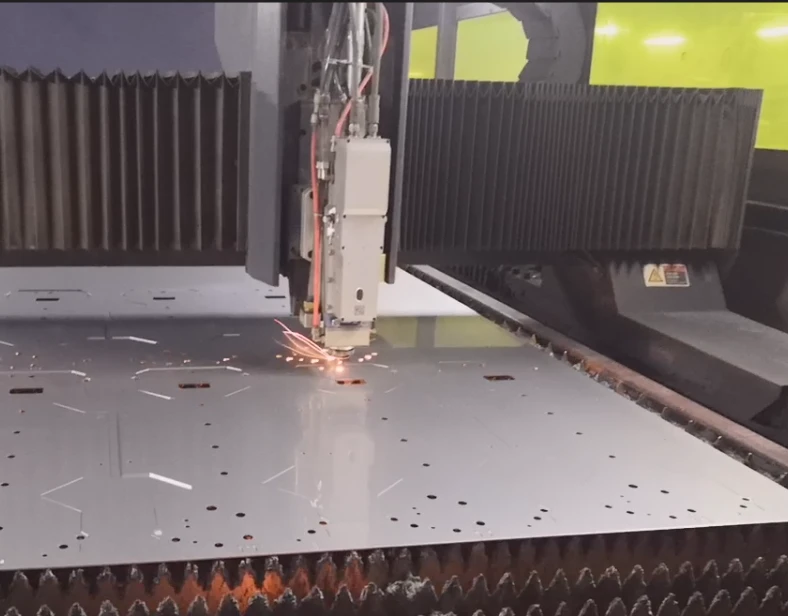
Working laser cutting machine
What is water jet cutting?
Water jet cutting uses a high-pressure jet of water ejecting from a tiny nozzle as a cutter. The water can be mixed with abrasives to enhance the cutting ability and accuracy with a tolerance of +/-0.2mm. Water jet cutting is doable for thick and low melting point sheet metal because it does not generate heat, which would melt the sheet metal.
Laser cutting vs. Water jet cutting
Laser cutting is five times more precise than water jet cutting. It is not only capable of cutting but also can engrave assembly marks on sheet metal. In the sheet metal fabrication industry, the minimum cutting slit of laser cutting is approximately 0.1mm, while water jet cutting is 0.5mm.
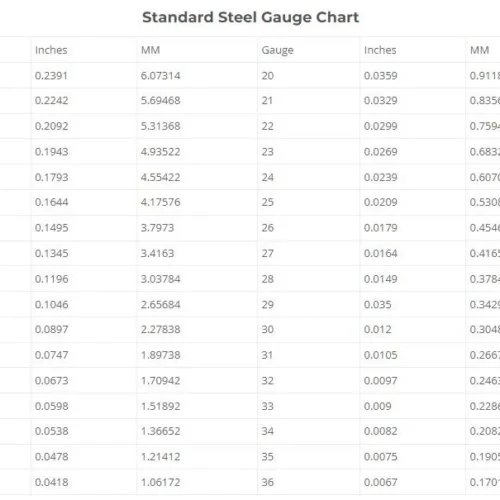
Water jet cutting is more efficient in rough machining, cutting thick sheet metal, while laser cutting is more precise machining. Water jet cutting allows cutting thicker sheet metal up to 25-30cm, while laser cutting only allows much smaller thickness. The maximum thickness that laser cutting can perform is only 6.07mm for sheet steel, followed by aluminum and galvanized sheet steel.
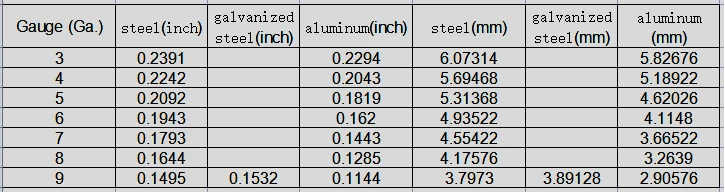
Gauge chart
Laser cutting Pros&Cons
Water jet cutting causes high noise pollution. Due to the mixed abrasives and water in the water jet cutting process, the working zone is very messy. Conversely, laser cutting is quieter and cleaner because the dust generated during the production process can be vacuumed directly.