There are dozens of machine processes used in manufacturing companies where raw and semi-raw materials create products. CNC turning and milling are among the most commonly used methods; like most machining processes, they require a machine.
In the past manual processes were carried out with a lot of work. The rise of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) has made the offer more advanced in precision and repeatability.
The two processes might seem similar but have different products as end products. This article will help better to understand the difference between CNC turning and milling. Stay tuned till the end.
What Are CNC Turning and CNC Milling?
CNC milling and turning can be considered synonymous, hence nearly a lot of similarities. But there are distinct, significant differences. Their functionality differs from one processing machine to the other. CNC turning is the production of parts faster and more affordable than milling.
Regarding the range of motion, CNC milling has limited cutting tools. Moreover, CNC turning materials are not conserved but allow faster production and complex design.
There are other differences between CNC milling and turning. They are the material used and the product produced. The two processes can be used as a complement to each other once the need arises.
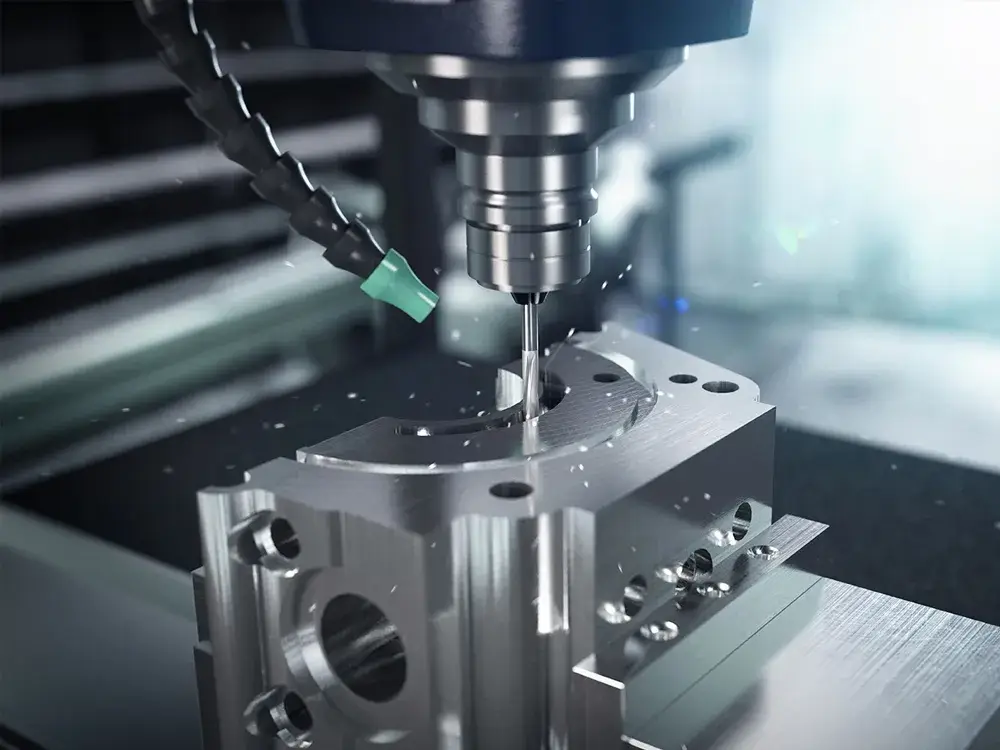

CNC milling
Milling is a machining process that uses rotary cutters to advance a blade to a workpiece by removing material. There are different types of milling machines, and CNC milling machines are one among them. The milling machine is chosen regarding the job at hand. But funding all milling machines in work station is hard since capital remains the biggest challenge.
Among the milling machine, CNC milling has occupied and replaced other machines like; drum milling machines, C-frame milling machines, and simplex milling machines since the technology has advanced hence new changes.
CNC milling is computerized, requiring minimal human interaction. The cutting tools are programmed, removing material from flat/ contoured surfaces, which enables it to be faster than manual processes. CNC milling is the best production machine.
CNC milling can produce complex shapes and ideal customized-design parts with the required detail, precision, and excellent surface finish.
At the same time, CNC milling has X, Y, and Z axes which help rotationally cut, and the workpiece remains stationary. This outcome has a limited dimensional operation which slows down the production process speed, making it suitable for prototyping and smaller production.
Milling can be classified into two divisions which include; face and peripheral. Face milling involves cutting action at or near the cutting tool corners. While in the peripheral case, the cutting action is along the diameter of the cutting tools.
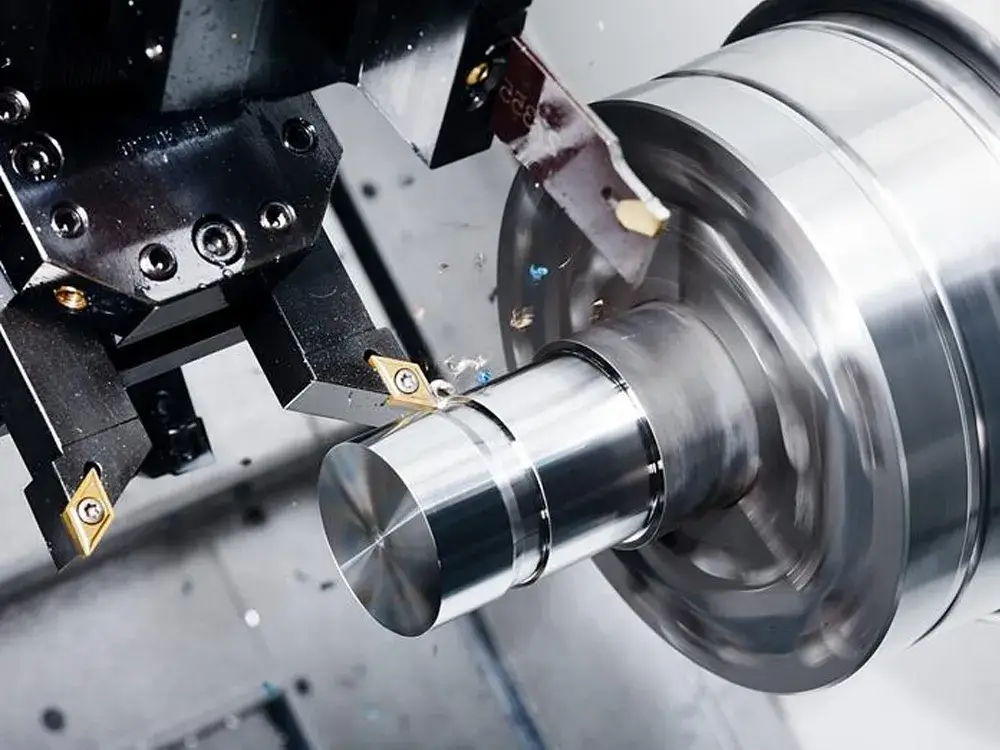
CNC turning
This is the most common lathe machining operation. The workpiece rotates during the CNC turning machine process while the cutting tools move linearly to produce cylindrical parts. The machine is fed up with a chuck of materials until a desired shape is attained. Removing material to achieve an end product is called subtraction machining.
The machine can complete the work using one side if there is only one turret on the CNC turning center. But for faster production, some turning centers have a central spindle and sub-spindle. Following this setting, the primary spindle partially machines the workpiece, submitted to the other sub-spindles that integrate to complete the remaining work on the other side.
Due to the required task, CNC turning is used for more significant workpiece production, hence used in more extensive operations. It also takes the shortest time possible to complete the assigned task.
Production capabilities
As listed below, CNC milling has many production capabilities, including a series of processes.
- Chemical
- Electrical
- Mechanical
- Thermal
Materials are efficiently conserved during CNC milling superior production. And the machine’s lifespan is increased, reducing material cost. The end products include; precision components and parts, short-run production, and prototype parts.
On the other hand, CNC turning lathes are used to conduct operations such as listed below;
- Boring
- Drilling
- Grooving
- Facing
- Parting
- Knurling
- Material fabrication
The difference between CNC turning and milling
Many might be wondering where the difference between CNC turning and milling exists. The significant difference is which part moves, either the machine itself or the raw material. In CNC milling processes, the cutting tools rotate while the material being involved is held up. While on the other hand, with CNC turning, the material rotates to create the desired shape, and the cutting tools remain stationary.
The explanation might be taken as simple words, but there is more than what meets the eye. Diving deeper into their differences will enhance many breakthroughs in how the processes are carried out, as stated below.
- First, let’s begin with the tool’s features: CNC turning contains a single-point cutting tool. While in CNC milling, there are multiple – points.
- Secondly, the uses: flat and irregular surfaces are considered to be produced by CNC milling. CNC turning is mainly viewed on conical or cylindrical materials.
- Thirdly, cutting: cutting involves a continuous process as the tools maintain constant contact with the workpiece in CNC turning. While in CNC milling, there is intermitted cutting with the tools continually engaging and disengaging the raw material from the cutting teeth.
- Lastly, chips: discontinuous chips are produced in CNC milling. While on the other hand, chips are made in intermittent, continuous, and fragmentation manner in CNC turning.
Since the differences have been stated orderly, it will be good to get deeper and understand these machining processes.
Similarities between CNC turning and milling
Both processes are among the most computerized machining processes. The process used to remove from the stock material the unwanted products: subtraction manufacturing.
Their end products are chips that are either discontinuous, continuous, or fragmented depending on the method used. However, the tools, machining methods, and stock material may differ per process.
The process uses the same developed Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology which has been programmed using Computer-Aided Design software (CAD). This introduction has helped to minimize human error since there is less supervision during operations. Manufacturers can deliver faster and more reliable consistent qualities.
There are a lot of qualities in the turning and milling process which can enable one to use them as a complement to each other. Then increasing the production of more materials with the best product.
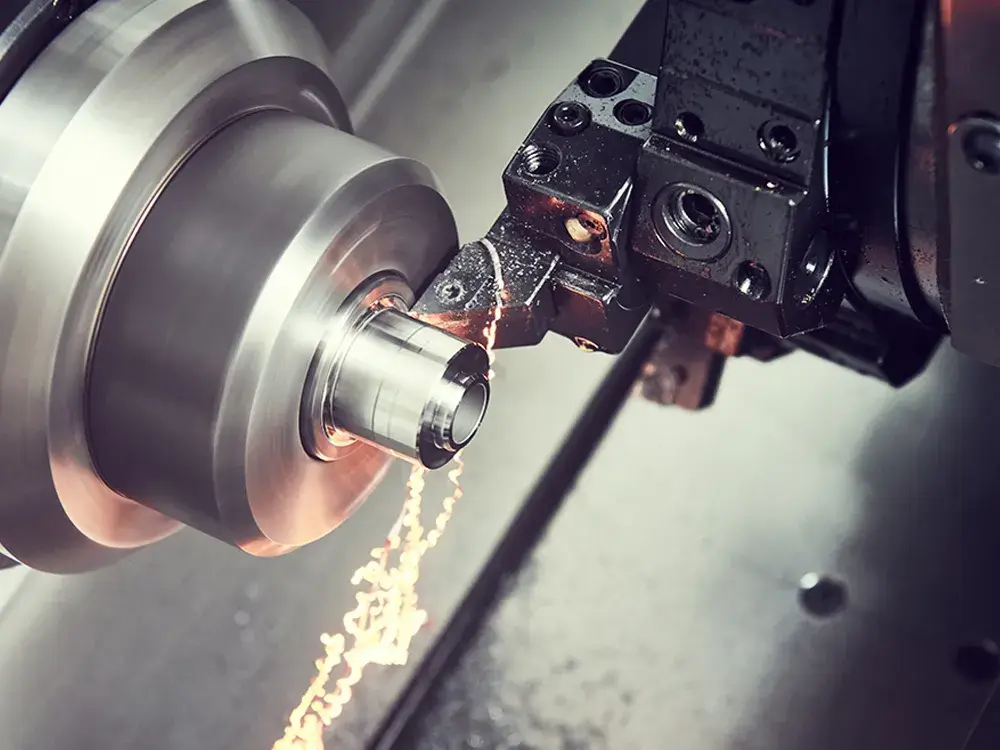

CNC turning distinctions
The machine of CNC turning holds the round bar and rotates as the chuck moves around. The speed will vary regarding the device and material used and each component’s features.
Rotating bar stock will be applied continuously on the stationary cutting tool, shaving away the unwanted material. During this process, several cutting tools will move in and around the stock bar to create the needed features.
CNC lathes will have various tooling option types, outer diameter limitations, and spindle options. The shapes are most likely round, with some hexagonal dimensions. All the spindle processes will join together to develop complete machine-needed features.
Due to the nature of the process and the tool used in cutting, the products can have different dimensions per design during the machining process. CNC turning parts are quicker to produce and more efficient than CNC milling parts which are smaller in quantity and quality.
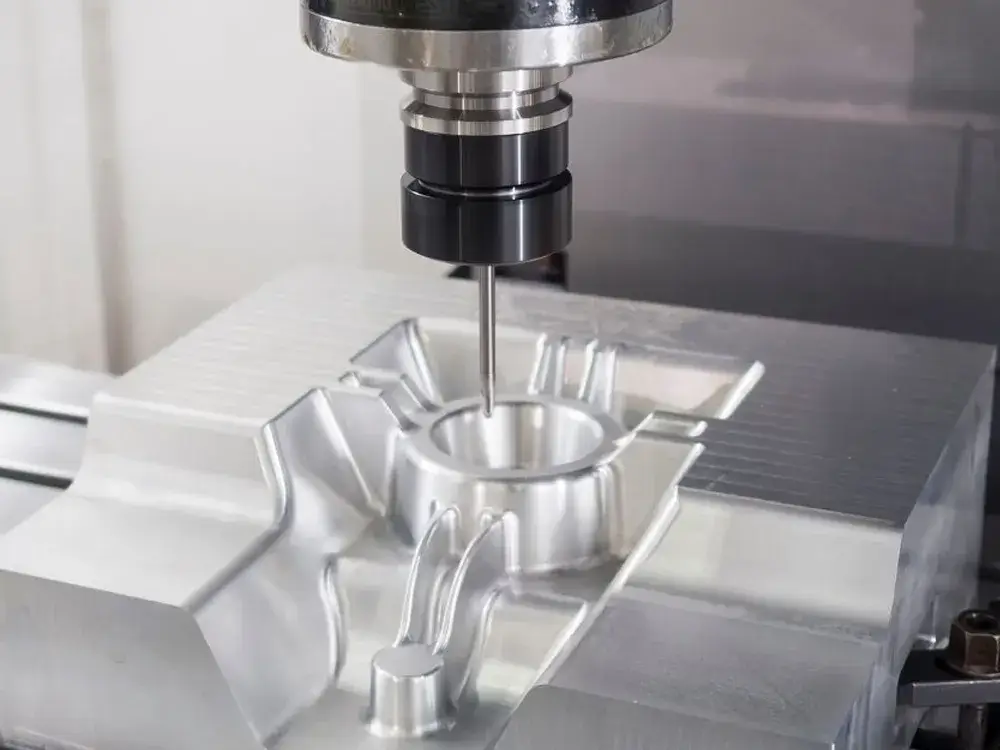

CNC milling
During this machining process, the workpiece remains stationary as the cutting tools continuously and rapidly rotate. The cutting tool is held by the spindle, which rotates at high speed, removing the materials.
The surfaces reserved for milling processes are flat or sculptured on square or rectangular blocks. This milling process is mainly used for small quantities.
Overview of CNC turning vs. milling
| Turning | Milling | |
| Method | Workpiece rotated | Cutting tool rotated |
| Results | cylindrical or conical | flat or sculptured |
| Machine | Lathe | milling machine |
| Tool | single point turning tool | multiple- point cutting tool |
| Contact | during the operation, the cutting tool remains in contact with the workpiece | the cutting tool is intermittent during the operation |
| Movement | cutting tool moves | workpiece moves |
| Waste | produces fragmented, discontinuous, or continuous chips | produces discontinuous chips |
Small milled features can sometimes be obtained from a piece of turning equipment which depends on the material type, overall complexity, and part size.
Ultimately the decision to use milling or turning depends on the design and features involved. The larger square flat part features will always be milled, while the cylindrical parts will be turned.
Industries using CNC milling and turning
Some industries support their machining processes: woodworking, the electrical sector, material fabrication, Electrical discharge machine (EDM), and Metal removal (in automotive or manufacturing). There are other industries involved; hence the list is endless.
Conclusion
The machining processes have differences; hence it is right to make a better choice before taking on a task. Thank you for sticking till the end; a comment or a question can be left regarding the processes.